🤖 These are the most commonly used CMD commands for Windows systems
What is CMD?
CMD is an acronym for Command. Command Prompt, or CMD, is the command line interpreter of Windows operating systems. It is similar to Command.com used in DOS called "MS-DOS Prompt."
Command Prompt uses the command line interface to communicate with the user. In the Windows operating system, this command prompt interface is implemented through the Win32 console.
In this blog, you can find the most commonly used and popular CMD commands for Windows systems.
Starting CMD in Windows
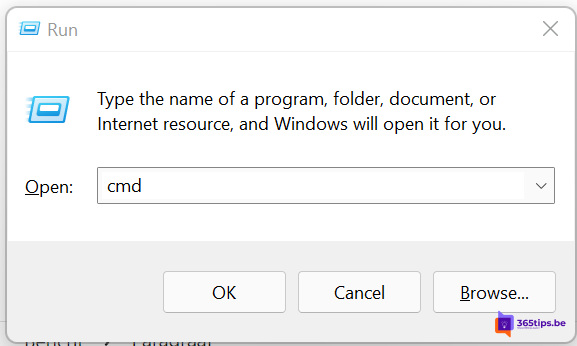
The user can open the interface via the CMD run command or by going to the original location C:【cmd.exe.
Or you can press Window key+R and then press CMD.
The most commonly used CMD commands
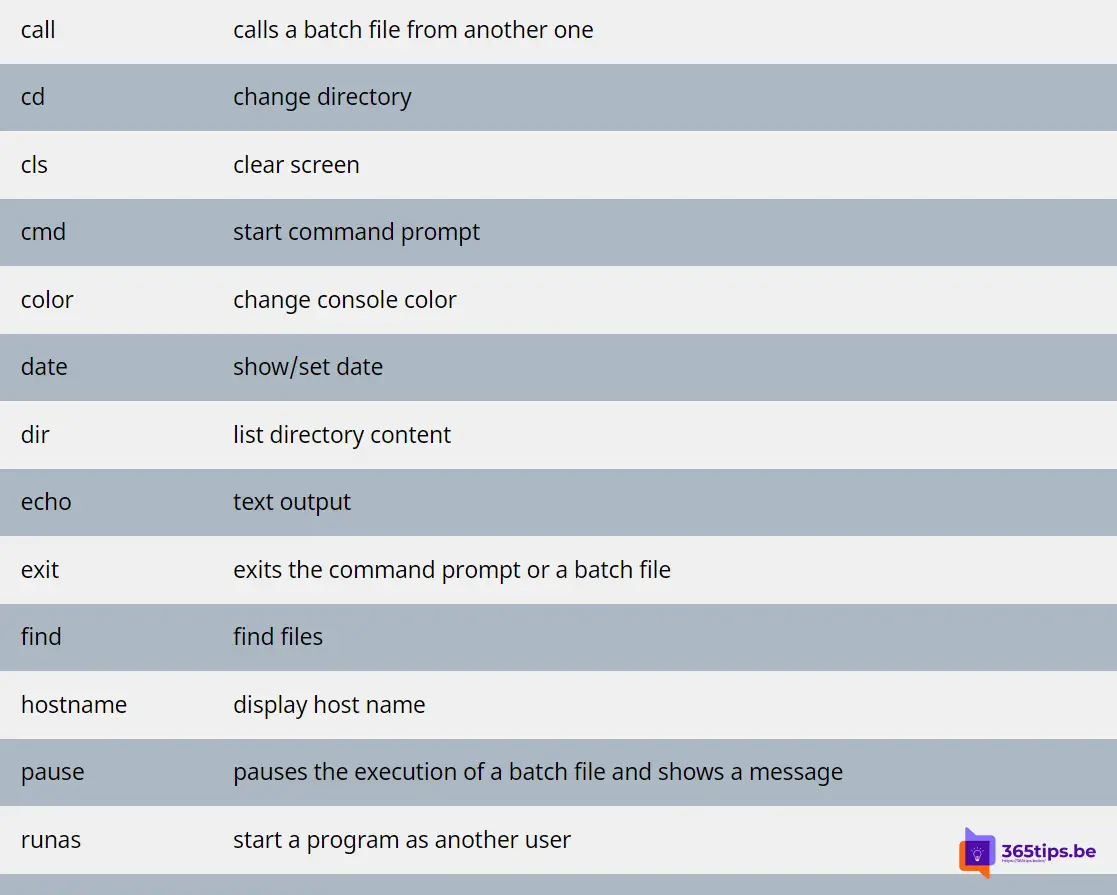
| call | calls a batch file from another one |
| CD | change directory |
| cls | clear screen |
| cmd | start command prompt |
| color | change console color |
| date | show/set date |
| dir | list directory content |
| echo | text output |
| exit | exits the command prompt or a batch file |
| find | find files |
| hostname | display host name |
| pause | pauses the execution of a batch file and shows a message |
| runas | start a program as another user |
| shutdown | shutdown the computer |
| sort | sort the screen output |
| start | start an own window to execute a program or command |
| taskkill | terminate a process or an application |
| tasklist | display applications and related tasks |
| time | display/edit the system time |
| timeout | wait any time |
| title | set title for prompt |
| far | display operating system version |
| w32tm | setting time synchronization/time server/time zone |
Network CMD commands
| ftp | transfer files to an FTP server |
| ftype | display file type and mapping |
| getmac | display MAC address |
| ipconfig | display IP network settings |
| netsh | configure/control/display network components |
| netstat | display TCP/IP connections and status |
| nslookup | query the DNS |
| pathping | test the connection to a specific IP address |
| ping | pings the network |
| route | display network routing table, add static routes |
| systeminfo | displays computer-specific properties and configurations |
| telnet | establish Telnet connection |
| tftp | transfer files to a TFTP server |
| tracert | trace routes similar to patchping |
Files CMD commands
| attrib | display file attributes |
| comp | compare file contents |
| compact | display/change file compression |
| copy / xcopy | copy files |
| diskcomp | compare content of two floppy disks |
| diskcopy | copy floppy disc to another one |
| erase / del | delete one or more files |
| expand | extract files |
| fc | copare files and display the differences |
| mkdir | create a new directory |
| move | move/rename files |
| rename | rename files |
| replace | replace files |
| rmdir / rd | delete directory |
| tree | display folder structure graphically |
| type | display content of text files |
Media commands
| chkdsk | check volumes |
| chkntfs | display/change volume check at startup |
| defrag | defragment media |
| diskpart | volume management |
| driverquery | display installed devices and their properties |
| format | format volumes |
| Tag | change volume name |
| fashion | configure interfaces/devices |
| mountvol | assign/delete drive mountpoints |
| verify | monitoring whether volumes are written correctly |
| full | show volume description and serial numbers of the HDDs |
Also read
Manage Microsoft Office 365 with PowerShell - Starter's Guide
How to install Azure AD preview module with PowerShell?
How to shut down, restart or put a Windows 11 PC into hibernate
How to install the new Exchange Online PowerShell V2 module ?
How to log in with Multi-factor Authentication on the Exchange Online PowerShell module?
